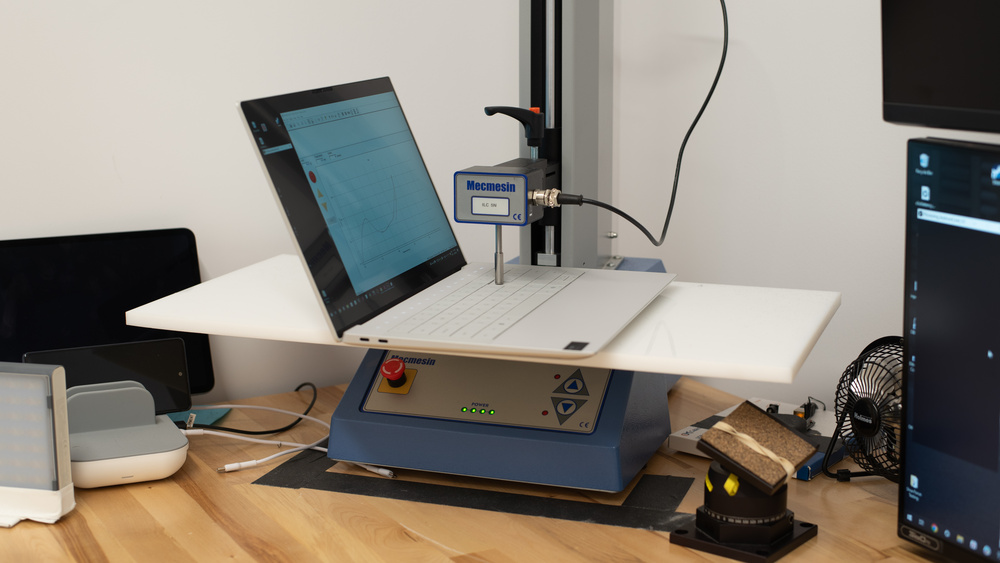
The Dell XPS 14 (2024) is a premium, thin, and light workstation laptop. The 14-inch model is a new addition to the XPS lineup, replacing the 15-inch Dell XPS 15 (2023). It's available with Intel Meteor Lake CPUs paired with Intel Arc integrated graphics only or with a discrete NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 Laptop GPU (6GB GDDR6, 40W /w Dynamic Boost). Display options include an FHD+ IPS panel and a 3.2k OLED panel; both are 120Hz screens with Dynamic Refresh Rate support. It has up-firing speakers, a 1080p webcam, Wi-Fi 6E wireless connectivity, and a 70Wh battery. Its port selection comprises three USB-C/Thunderbolt 4s and a MicroSD card reader.
See our unit's specifications and the available configuration options in the Differences Between Variants section.
Our Verdict
The Dell XPS 14 is great for school use. Its compact design makes it easy to carry around, and its battery lasts easily through a full day of light use. It provides a good user experience overall, though its edge-to-edge keys and invisible touchpad might take some time to get used to. Its Intel Meteor Lake CPU can easily handle general productivity tasks like text processing, web browsing, and video playback, as well as more demanding workloads like programming. You can also perform GPU-intensive tasks like 3D graphics and video editing, as it's available with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 Laptop GPU; however, you might not get the best experience if the work is overly complex, as its performance is limited in favor of a compact and sleek design with a smaller cooling system.
-
Sleek, compact design.
-
Bright display.
-
Outstanding webcam.
-
CPU can handle some demanding tasks.
-
All-day battery life.
-
Keyboard and touchpad design requires some adaptation.
-
Discrete GPU option limited to a low-power (30W) RTX 4050.
-
No USB-A or HDMI port.
The Dell XPS 14 isn't designed for gaming. Although it's available with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 Laptop GPU, it'll struggle to push over 60 fps at 1080p in highly demanding games, as the RTX 4050 is an entry-level GPU and runs at a low wattage. As for the display options, the FHD+ IPS panel has a slow response time, and none of the displays support FreeSync or G-SYNC to reduce screen tearing. On the upside, it doesn't get hot or loud under load.
-
120Hz display.
-
CPU can handle some demanding tasks.
-
Doesn't get hot or loud under load.
-
Fast, user-replaceable SSD.
-
Can only handle light or older titles at 1080p with low settings.
-
Soldered RAM.
-
IPS panel has slow response time.
-
No VRR.
-
No USB-A or HDMI port.
The Dell XPS 14 is good for media consumption. It's very portable, thanks to its compact design, and its battery lasts almost 14 hours of video playback, giving you plenty of time to get through multiple movies and TV show episodes. You can get the laptop with an FHD+ IPS or a 3.2k OLED panel. The latter will provide a better viewing experience, as it looks sharper and more colorful, with deeper, inky blacks. Unfortunately, the speakers have almost no bass, and while they get very loud, they sound unpleasant and sibilant at higher volume levels.
-
Sleek, compact design.
-
Bright display.
-
Available with sharper OLED touchscreen.
-
Loud speakers.
-
All-day battery life.
-
IPS panel isn't ideal for dark room viewing.
-
Speakers lack bass.
-
Speakers sound sibilant at higher volume levels.
The Dell XPS 14 is great for use as a workstation. Its Intel Meteor Lake CPU and NVIDIA discrete GPU have enough processing power to handle intensive tasks like video editing, programming, and 3D animation. However, you might not get the smoothest experience if the work is overly complex, as the RTX 4050 is an entry-level graphics processor, and this variant runs at a low Total Graphics Power (TGP). You can do color work, though you'll have to spend extra to get the nicer 3.2k, 100% DCI P3 OLED display, as the base FHD+ IPS only has full sRGB coverage. Its port selection is okay; you get three USB/Thunderbolt 4s, but it only has a MicroSD card reader instead of a full-size one, and there's no HDMI port. It doesn't get hot or loud under load, and while there's some thermal throttling, it's relatively minimal.
-
CPU can handle some demanding tasks.
-
Doesn't get hot or loud under load.
-
OLED panel is suitable for color-critical work.
-
Fast, user-replaceable SSD.
-
Thunderbolt 4 support.
-
Discrete GPU option limited to a low-power (30W) RTX 4050.
-
Soldered RAM.
-
CPU throttles under load.
-
No USB-A or HDMI port.
The Dell XPS 14 is great for business use. It has a remarkably sturdy build, a compact design, and all-day battery life, making it well-suited for those who travel a lot for work. Its Intel Meteor Lake CPU can easily handle general productivity tasks like text processing, web browsing, spreadsheets, and presentations. You can also get an optional NVIDIA RTX 4050 discrete GPU, which will give you enough processing power to do some video editing for your business. The overall user experience is good, though it may take some time to get used to its edge-to-edge keys and invisible touchpad. It has an excellent 1080p webcam for video calls, as well as a fingerprint sensor and facial recognition for quick logins.
-
Sleek, compact design.
-
Bright display.
-
Outstanding webcam.
-
All-day battery life.
-
Keyboard and touchpad design requires some adaptation.
-
No USB-A or HDMI port.
- 8.4 School
- 7.3 Gaming
- 7.6 Multimedia
- 8.1 Workstation
- 8.2 Business
Changelog
-
Updated Dec 06, 2024:
Added mention of the Apple MacBook Pro 14 (2024) as an alternative with a wider port selection in the Ports section.
- Updated Jun 05, 2024: Added mention of the ASUS ROG Zephyrus G14 (2024) as an alternative with faster GPU options in the GPU section.
- Updated May 27, 2024: Added mention of the Dell XPS 16 (2024) as an alternative with a larger display in the Screen Specs section.
- Updated May 23, 2024: We've increased the Ease of Access score in the Serviceability section from 7 to 7.5 because Dell provides service instructions in its owner's manual.
- Updated May 17, 2024: Review published.
Differences Between Sizes And Variants
We tested the Dell XPS 14 (model 9440) with an Intel Ultra Core 7 155H CPU, integrated Intel Arc graphics, 16GB of RAM, and 512GB of storage. The CPU, GPU, memory, and storage are configurable; the available options are in the table below.
| Screen |
|
|---|---|
|
CPU |
|
| GPU |
|
| Memory |
|
| Storage |
|
| Color |
|
See our unit's label here.
Compared To Other Laptops
The Dell XPS 14 2024 is a good laptop overall. It feels remarkably well-built, and it's arguably one of the sleekest laptops on the market design-wise. However, its design comes at the cost of usability and performance. Also worth noting is the base FHD+ display configuration option. While there are benefits to the lower resolution IPS panel (easier to drive, lower power consumption), it feels rather cheap on such a premium device, especially when competitors are offering higher quality OLED panels at no additional cost.
See our recommendations for the best workstation laptops, the best video editing laptops, and the best laptops for photo editing.
The Dell XPS 13 (2024) and the Dell XPS 14 (2024) are premium ultraportables nearly identical in design but offer vastly different performance. Whereas the 14-inch model is capable of handling some demanding workloads, the 13-inch model is only suited to light productivity tasks. While both laptops offer the same Intel Ultra Core processors under the hood, Dell's cooling solution for the XPS 13 is inadequate, resulting in significant thermal throttling. Dell also offers additional dedicated GPU options on the XPS 14 for those whose workflow includes video editing, programming, and 3D animation. Other niceties on the 14-inch include up-firing speakers and superior battery life (on the IPS panel, the OLED option will likely drain the battery faster).
The Dell XPS 14 (2024) is a new addition to the XPS lineup and replaces the Dell XPS 15 (2023). While the 14-inch model is more compact and easier to carry, its new design may not be to everyone's liking. For example, its edge-to-edge keys and invisible touchpad both require a fair amount of adaptation to use properly. The 14-inch model also takes a step back in its port selection, ditching the 15-inch's full-size SD card reader for a MicroSD reader. Performance-wise, you can get more performance out of the older 15-inch model if you go with the higher-end configurations. That said, the 14-inch model's Intel Meteor Lake CPUs are more efficient, resulting in much longer battery life and better thermals.
The Dell XPS 14 (2024) and ASUS Zenbook 14 OLED (2024) are similar premium ultraportable laptops. They both feature outstanding build quality with an all-aluminum chassis. The Dell offers far superior battery life, webcam performance, and microphone performance, making it a better choice for those who need to use their laptop on the go. By contrast, the ASUS comes standard with an OLED display, which is a big upgrade over the Dell's FHD+ IPS display. The ASUS also offers much better connectivity options, including an HDMI output, which makes it better for at-home or office use.
Although both are 14-inch Windows laptops available with Intel Meteor Lake CPUs, the Dell XPS 14 (2024) and the HP Spectre x360 14 (2024) are quite different. The XPS 14 is more of a thin and light workstation designed to handle more demanding workloads like programming and video editing on the go, while the Spectre x360 is a 2-in-1 ultraportable designed for light, general productivity tasks. In other words, you can get more performance out of the XPS 14. However, the Spectre x360 provides a better user experience, as its keyboard and touchpad are easier to use. The XPS 14 has a slightly sharper OLED panel option, but you have to pay extra for it, as the base display option is an FHD+ IPS panel, whereas the Spectre x360 comes with a 2.8k OLED at no additional cost.
The ASUS ROG Zephyrus G14 (2024) is better than the Dell XPS 14 (2024) for most uses. The G14 has more GPU options, giving you a smoother gaming experience and more processing power to tackle demanding productivity tasks. It also provides a better user experience, as its keyboard and touchpad are easier to use and require less adaptation. The G14's OLED panel isn't quite as sharp as the XPS 14's OLED panel; however, you don't have to pay extra for the G14's OLED display, whereas the XPS 14's OLED panel is a premium option that costs more.
Though the Apple MacBook Air 15 (2024) and Dell XPS 14 (2024) are both premium thin and light laptops, the Apple is better in most ways for most people. The Apple laptop's M3 silicon can handle some heavier workloads, but the fanless design limits its performance headroom, so it's really best for general productivity tasks. It also offers a much better user experience overall; it features a better keyboard and display by default, as well as industry-leading speakers and haptic touchpad. The Dell features more powerful hardware, including options for dedicated GPUS, making it better suited for workstation tasks. While you can get a nicer OLED display on the Dell, you have to pay extra for it.
The Lenovo ThinkPad X1 Carbon Gen 11 (2023) and Dell XPS 14 (2024) are similar high-end 14-inch ultraportable Windows laptops. They excel at general productivity tasks but can each handle the occasional demanding workload. The Dell outperforms the Lenovo model for productivity tasks as its discrete GPU provides more versatility for tasks like video rendering. Both laptops come with displays suitable for color correction work and offer outstanding build quality. The Lenovo ultimately provides a superior user experience, as its keyboard and trackpad are much easier to use; the edge-to-edge keys and invisible touchpad on the Dell require a fair amount of adaptation to use properly.
The Dell XPS 16 (2024) and the Dell XPS 14 (2024) are very similar design-wise and provide a similar user experience overall. Other than size, the main differences between these two laptops are the configuration options and the amount of processing power you can get. The XPS 16 is a larger device with a superior cooling system, so it's available with a faster Core Ultra 9 CPU and higher-end NVIDIA discrete GPUs, like the RTX 4060 and 4070.
The Apple MacBook Pro 14 (2024) is better than the Dell XPS 14 (2024) for most uses. The MacBook Pro has a lot more processing power, allowing it to tackle significantly more demanding tasks. It also provides a superior user experience overall, sporting a brighter display, a wider port selection, and better-sounding speakers. While both laptops have a tactile keyboard and a haptic touchpad, the XPS 14 requires more adaptation, as its edge-to-edge keys can cause more typos, and its invisible touchpad is hard to locate at times. Though neither is ideal for gaming, you can play some games on these machines, and each has its advantage; the MacBook Pro 14 has more processing power to deliver smoother gameplay, especially if you go with one of the higher-end configurations, but far more games run on Windows than macOS.
The Apple MacBook Pro 14 (M3, 2023) is much better than the Dell XPS 14 (2024). The MacBook Pro 14 provides a better user experience, as its keyboard and touchpad are easier to use, and its wider port selection makes it easier to connect peripherals and external displays, so you don't have to carry dongles or adapters. You can also get more performance out of the MacBook Pro 14, especially on the GPU side. Neither of the XPS 14's display options (IPS and OLED) gets as bright as the MacBook Pro's Mini LED screen. Also, you have to pay extra to upgrade to the nicer 3.2k OLED panel on the XPS 14; otherwise, you only get an FHD+ IPS display, which is nowhere near as good as the MacBook Pro 14's screen.
The Dell XPS 14 (2024) and the HP OMEN Transcend 14 (2024) are very different laptops. The Dell is a productivity-focused model, while the HP is primarily a gaming laptop that can also double as your work laptop. Although both models can handle fairly demanding tasks, like video editing and 3D modeling, the HP will give you better performance, as it's configurable with up to an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4070, while the Dell is only available with integrated graphics or an RTX 4050. The HP provides a better user experience overall, as its keyboard and touchpad are easier to use and adapt to. It also has a wider port selection to connect multiple peripherals and external displays. However, the Dell has a much better webcam and longer battery life.
The Dell XPS 14 (2024) and Apple MacBook Air 13 (2024) are premium laptops targeting different uses. The Dell is a thin, light laptop capable of performing more demanding workloads like video editing or 3D animation. In contrast, the Apple laptop shines as an ultraportable for light productivity tasks and media consumption (even if the M3 SoC can handle the occasional demanding workload). In this sense, the Apple model provides a better user experience with its better battery life, brighter display, and great haptic touchpad. However, the Dell sports a better port selection and a wider range of hardware, including user-replaceable RAM and storage.
Though both are 14-inch models, the ASUS Zenbook 14 Flip OLED (2023) and the Dell XPS 14 (2024) are quite different. The Zenbook is a 2-in-1 convertible designed for general productivity, while the XPS 14 is a more traditional clamshell model intended for slightly more demanding tasks, like programming and video editing. Regarding the overall user experience, the Zenbook is better, as the XPS' keyboard and touchpad design requires a fair amount of adaptation and might not be to everyone's liking. The Zenbook also has a wider port selection, making connecting peripherals and external displays easier. While the XPS 14's battery life is much longer than the Zenbook's, the difference is likely much smaller if you get the XPS with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 discrete GPU. Also worth noting is that the XPS 14's base configuration comes with a lower resolution FHD+ display; you have to pay more for the 3.2k OLED panel.
The Lenovo Slim Pro 7 14 (2023) and the Dell XPS 14 (2024) are both compact laptops designed for general productivity (text processing and web browsing) as well as moderately demanding workloads, like video editing and 3D modeling. The Dell's build feels more premium, but the overall user experience isn't quite as good as the Lenovo's, as its keyboard and touchpad design requires a fair amount of adaptation and might not be to everyone's liking. Also, the Dell laptop's base configuration comes with a lower resolution FHD+ display (you must pay more for the higher-end OLED panel), whereas the Lenovo starts with a QHD+ panel, with the option to upgrade to a 120Hz 3k screen. The Lenovo also has a wider port selection, including an HDMI 2.1 port. As for performance, the Dell is better, but only if you get a configuration with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 GPU, and even then, the difference is relatively small.
While the Lenovo Legion Pro 5 Gen 8 16 (2023) and Dell XPS 14 (2024) feature powerful hardware, they're quite different. The Lenovo is a 16-inch mid-range gaming laptop with hardware capable of performing workstation tasks, while the Dell is a premium 14-inch thin and light workstation. The Lenovo offers a great user experience with a big keyboard and touchpad and high refresh rate QHD+ IPS displays. However, it's a big, bulky device with terrible battery life. By contrast, the Dell laptop offers capable hardware in a small, portable form factor. This makes it the better choice for professionals. Its build quality is outstanding, and this model offers all-day battery life for light tasks. However, the keyboard and touchpad are worse than those of the Lenovo, as they require a steep adaptation period.
The Dell XPS 14 (2024) is much better than the Dell Inspiron 14 (2023). The XPS is a more premium model with a sturdier build and sleeker design, while the Inspiron is a mid-range model with some compromises, like a lower-quality webcam and a weaker cooling system. Both are productivity-focused laptops; the main difference is that the XPS has more processing power, allowing you to tackle more demanding tasks like programming and video editing.
The Lenovo LOQ 15 (2023) and Dell XPS 14 (2024) are very different devices. The Lenovo is a budget 15-inch gaming laptop, while the Dell is a premium 14-inch thin and light workstation. Depending on how you configure the Lenovo, its performance and user experience will drastically change. Its base 60Hz 1080p IPS isn't suited for gaming, and its entry-level RTX 3050 is fine for light or esports titles but can't deliver consistent performance for modern AAA games without significantly tweaking the settings. By contrast, the Dell model offers powerful hardware, outstanding build quality, and a 3.2k OLED display option with DCI P3 coverage; it's suited for performing workstation tasks on the go.
The Apple MacBook Air 13 (2022) is better for most people than the Dell XPS 14 (2024). The Apple is a 13-inch ultraportable designed for general productivity tasks. It offers a much better keyboard and haptic touchpad, exceptional battery life, and a better display with DCI P3 coverage; this makes it suitable for color correction work. By contrast, the Dell model has options for more powerful hardware, making it suitable for workstation tasks on the go. While you can configure the Dell with a sharper 3.2k OLED panel than the Apple laptop's IPS display, you have to pay extra for it.
The Dell XPS 13 Plus (2022) and the Dell XPS 14 (2024) are very similar in design and provide a similar user experience. The main difference is that the XPS 14 is more of a workstation designed for more demanding tasks like video editing and programming on the go, while the XPS 13 Plus is an ultraportable for light productivity tasks like text processing and web browsing. The XPS 14 is available with faster Intel Meteor Lake CPUs and an NVIDIA discrete RTX 4050 Laptop GPU, and its superior cooling system allows for better thermals and performance in sustained workloads. Intel's Meteor Lake CPUs are also more efficient, resulting in significantly longer battery life on the XPS 14.
Despite both offering portable form factors, the Apple MacBook Air 13 (M1, 2020) and Dell XPS 14 (2024) cater to different needs. Despite its age, the Apple laptop is better for most users as it excels at general productivity tasks. The Apple model offers a better user experience thanks to its exceptional portability, better keyboard and haptic touchpad, and better display and speakers. By contrast, the Dell has better performance, making it better-suited to those with heavy workloads. It also has an option for a 3.2k OLED display, which offers complete DCI P3 coverage, but you have to pay extra to get it.
The ASUS ROG Zephyrus G14 (2022) and Dell XPS 14 (2024) are 14-inch laptops designed for different purposes. The ASUS is a gaming laptop whose powerful hardware makes it suitable for demanding workloads like 3D rendering or video editing. The ASUS has multiple IPS high refresh rate display options with variable refresh rate support, AMD Ryzen 7 or 9 6000 series CPUS, and a few Radeon 6000-series GPU options. By contrast, the Dell is an ultraportable laptop designed for general productivity tasks; however, depending on your chosen configuration, it can tackle the occasional demanding workload or gaming session. The Dell features Intel's new Meteor Lake CPUs, up to an NVIDIA RTX 4050 GPU, and an FHD+ 120Hz IPS panel or 3.2K 120Hz OLED display with dynamic refresh rate support. This isn't the same as variable refresh rate, so you'll likely see some tearing when playing games with an uncapped frame rate.
Test Results
The Dell XPS 14 is available in a Platinum or Graphite color. See the bottom of the laptop here.
The Dell XPS 14's build quality is outstanding. Its all-aluminum chassis feels very sturdy, exhibiting only a small amount of flex on the lid and none on the keyboard deck. The display doesn't twist when manipulating it. The finish is relatively scratch-resistant; fingerprints aren't an issue, either, though the Graphite model is likely worse in that regard.
Accessing the internals is relatively easy; you only need to remove eight T5 screws and undo the bottom panel's clips. A prying tool isn't necessary as long as you're careful. The SSD slot supports M.2 2230 and 2280 PCIe Gen 4 NVMe SSDs.
Get the owner's manual here.
The Dell XPS 14 is available with the following displays:
- 14.5" IPS 1920 x 1200 120Hz (100% sRGB)
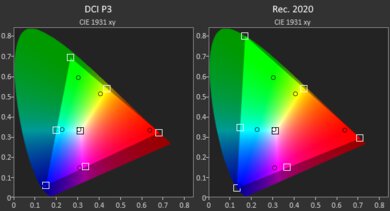
- 14.5" OLED 3200 x 2000 120Hz (Touchscreen, 100% DCI P3)
The FHD+ IPS panel looks reasonably sharp on a 14.5-inch screen. You can see individual pixels, even at typical viewing distances, which might bother you if you're used to higher resolution panels like Apple MacBooks' Retina displays. The OLED panel, which has a pixel density of 260 PPI, looks much sharper. Both panels have a 16:10 aspect ratio. This format is great for productivity, giving you slightly more vertical space than a standard 16:9 display, allowing you to see more information when reading a document or website. The OLED panel is susceptible to permanent burn-in, especially with static elements like Windows' taskbar; however, it's unlikely to be an issue for those viewing varied content. Check out the Dell XPS 16 (2024) if you want a similar laptop with a bigger screen.
Both display options have a 120Hz refresh rate. Though not entirely necessary, this high refresh rate does improve the user experience, as it makes motion look smoother (when scrolling through a document) and input feel more responsive (when moving the mouse cursor and using touch input) than a standard 60Hz display. The IPS panel has a slow response time, resulting in visible ghosting behind fast-moving objects. The OLED panel has a much faster response time, as most OLEDs do. Dynamic Refresh Rate allows the screen to change the refresh rate, depending on what you're doing and whether you have the laptop plugged in or running on battery. This isn't the same as FreeSync or G-SYNC, so you'll likely see some tearing when playing games with an uncapped frame rate.
The IPS panel has a good contrast ratio, measuring slightly above the average for this type of display. However, it's still pretty low compared to other display technologies like VA and OLED. This contrast level makes blacks look gray in dim settings. The OLED has an effective infinite contrast ratio since it can turn off individual pixels to produce perfect blacks.
The IPS panel gets bright enough for use in most indoor environments. Outdoor use is possible during the day, but you may have trouble seeing some content, especially content with dark colors. It gets very dim at the lowest brightness setting, which helps reduce eye strain when viewing content in the dark. The OLED panel has a lower advertised brightness of 400 cd/m².
While the IPS panel technically has a matte finish (Dell refers to it as 'anti-glare'), it looks and behaves like a cross between a glossy and matte display, so it's better at handling direct, mirror-like reflections than a true glossy finish, but it doesn't suffer from the halo-like effects around bright objects often seen on matte finishes. The OLED panel has a glossy finish and is likely worse at handling direct reflections.
The IPS panel's horizontal viewing angle is good. The image remains accurate until you reach a moderately steep angle to the left or right. You can share color-critical work with someone else as long as the other person isn't too far off to the side. The OLED panel is likely better in regards to color washout and brightness loss but will suffer more from color shift, similar to the Dell XPS 13 Plus (2022).
The IPS panel's vertical viewing angle is decent. Like the horizontal viewing angle, the image remains accurate until you look at it from a moderately steep angle from above or below. The OLED panel won't dim or wash out as much, but it'll suffer more from color shift.
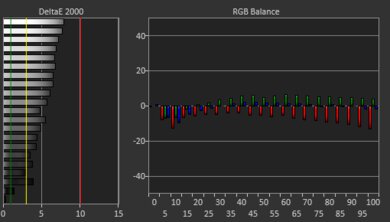
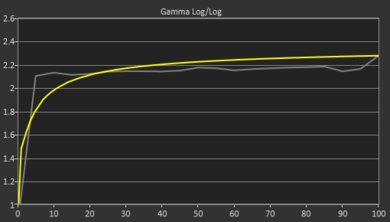
The FHD+ IPS display's out-of-the-box accuracy is sub-par. Most color inaccuracies are relatively minor; it's mainly the white balance that's off, especially at higher brightness levels. The color temperature is slightly cooler than the standard 6500K target, giving the image a slight, almost imperceptible, blueish tint. The gamma isn't too far off the curve—most scenes are a tad too bright, while dark scenes are too dark.
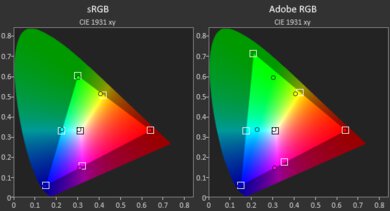
The FHD+ IPS display is an sRGB panel, meaning it only has full coverage of the commonly used sRGB color space. If you need to do any type of content creation work, like photo and video editing, it's best to go with the OLED panel, as it has full DCI P3 coverage.
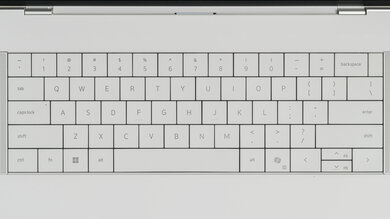
The Dell XPS 14 has a good keyboard. Except for a few, most keys are very stable. They have an adequate amount of key travel (not as short as MacBooks, but could use a bit more), require little force to actuate, and provide clear tactile feedback. The main problem is the layout. Although it feels spacious, the size of certain keys, like Caps Lock, can take some time to get used to. Also, the power button is right next to Backspace, so it's easy to hit it by accident. That said, you can change the behavior of the power button so that it requires a longer press to activate. Another aspect that'll require adaptation is the edge-to-edge keys. The lack of space between the keys means there's a higher chance of hitting an adjacent one, and the keycaps are almost completely flat, making it hard to feel the center of each key. This laptop uses a capacitive function row. It shows the function keys by default; you can activate the media shortcuts by pressing Fn. You can also lock the capacitive row to the shortcuts by pressing Fn and Esc.
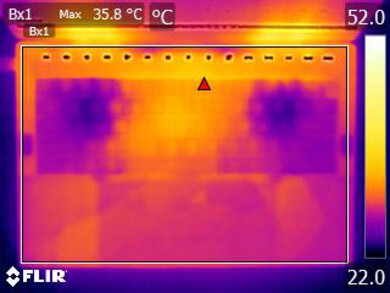
The Dell XPS 14 has a decent touchpad. Like the Dell XPS 13 Plus (2022), the entire deck is a single piece of glass, so there's no indication as to where the touchpad starts and ends. Here's an approximation of where the touchpad is. You can also see it faintly in this thermal image. The tracking is okay; it isn't always responsive around the edges, though that could be simply because it's hard to know if you're at the edge without looking. Palm rejection is also a bit of a hit-or-miss. You can click anywhere since this is a haptic touchpad, meaning it has a haptic engine to simulate clicks instead of physical buttons. The haptic feedback is good; no complaints there.
The Dell XPS 14's speakers sound clear and natural but have very little bass. Volume-wise, they get very loud; however, they sound rather unpleasant and sibilant at higher volume levels.
The Dell XPS 14 2024 has an excellent webcam. The image looks detailed and well-exposed. The colors are vibrant and saturated, though the color temperature is quite warm. Voices sound loud and clear over the microphone, with no noticeable static or background noise.
The Dell XPS 14 has an okay port selection. All three USB-Cs support Thunderbolt 4 (up to 40 Gbps data transfer speed and two 4k display @ 60Hz), DisplayPort 1.4, and Power Delivery. The latter allows for fast charging of the laptop and other PD-supported mobile devices. The laptop comes with a USB-C to USB-A/HDMI combo adapter. Check out the Apple MacBook Pro 14 (2024) if you want a similar laptop with more ports.
The Dell XPS 14 2024's wireless adapter is an Intel Killer 1675 (AX211). Wi-Fi 6E gives access to the 6GHz band, providing faster speeds, lower latency, and less signal interference than previous Wi-Fi standards. However, you need a router that supports Wi-Fi 6E to benefit from these features.
The Dell XPS 14 is available with the following CPUs:
- Intel Core Ultra 7 155H (16 cores, 22 Threads, up to 4.8 GHz, 24MB Cache)
- Intel Core Ultra 7 165H (16 cores, 22 Threads, up to 5.0 GHz, 24MB Cache)
Both are high-performance CPUs from Intel's Meteor Lake family. Unlike Intel's 14th Gen processors (13th Gen Raptor Lake refreshes), these CPUs have two low-power E-cores (LP-E) to further improve efficiency and an NPU (Neural Processing Unit) to speed up AI-based tasks, like background-blurring on video calls and image generation in some photo editing apps. They can handle general productivity tasks, like text processing, web browsing, video playback, and spreadsheets, as well as more demanding workloads like programming and video editing. That said, they're far from being the fastest CPUs on the market. If you have an extremely demanding workload, you're still better off getting a laptop with a higher-wattage CPU, like the Dell Alienware m18 R2 (2024). Core composition is the same on both CPUs; they both have six performance cores, eight efficiency cores, and two low-power efficiency cores (6P+8E+2LP-E). The only difference is that the 165H has slightly faster clock speeds, which typically results in only a small performance boost.
The Dell XPS 14 is available with Intel Arc integrated graphics only or with a discrete NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 Laptop GPU (6GB GDDR6 VRAM, 30W TGP). Intel's Arc graphics can only handle light productivity tasks. The RTX 4050 gives you enough processing power to tackle more demanding workloads like video editing and 3D modeling, but just barely, as the RTX 4050 is an entry-level discrete GPU, and it runs at a TGP (Total Graphics Power) of 30W (40W with Dynamic Boost), which is at the very low end of NVIDIA's recommended 35W–115W power range. In other words, it can get the job done, but don't expect the smoothest experience or the fastest rendering or completion times. The same goes for gaming; the RTX 4050 can handle some demanding games at 1080p; however, you'll have to play with low settings and rely on DLSS/Frame Generation to get playable frame rates. Check out the ASUS ROG Zephyrus G14 (2024) if you need a compact laptop with faster GPU options.
You can configure the Dell XPS 14 with 16GB, 32GB, or 64GB of RAM. The 16GB and 32GB models use 6400MHz modules, while the 64GB models use 7467MHz modules. The memory isn't user-replaceable.
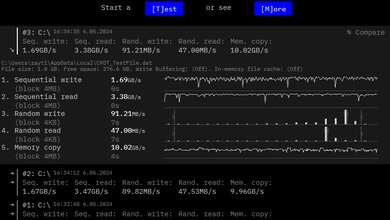
You can configure the Dell XPS 14 with 512GB, 1TB, 2TB, or 4TB of storage. The SSD is user-replaceable; the slot supports M.2 2230 and 2280 PCIe Gen 4 NVMe SSDs.
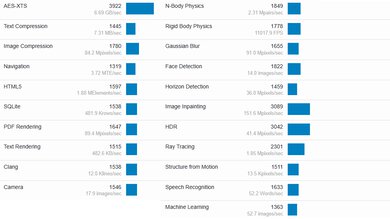
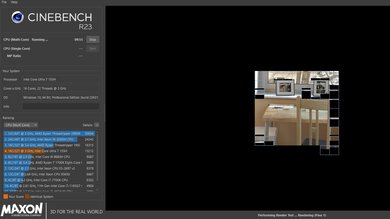
The Dell XPS 14's Intel Core Ultra 7 155H CPU scores well in Geekbench 5. This performance level is somewhere between a high-end ultraportable and a workstation, meaning it's better than most thin and light laptops designed for general productivity, but it's at the lower end when compared to workstation laptops with a higher wattage CPU and a superior cooling system. It'll handle demanding workloads; just know there are significantly faster CPUs on the market. You can easily find last-gen models that perform better if you're willing to compromise a bit on portability. The NPU (Neural Processing Unit) might help in some tasks, though few applications make use of it at the time of writing. Switching to the Ultra Performance mode has no impact on the scores in these benchmarks. As for GPU-intensive tasks, the integrated Intel Arc GPU performs poorly. The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 is better, but as mentioned in the GPU section, don't expect too much of it since it's an entry-level GPU running at a low wattage.
The Dell XPS 14 scores well in the Cinebench R23 benchmarks. Again, the Intel Core Ultra 7 155H's multi-thread performance is certainly better than what you can get in most thin and light laptops, but it isn't particularly impressive compared to higher wattage CPUs, performing worse than the older Intel Core i7-13700H in the Dell XPS 15 (2023). Switching to the Ultra Performance mode has minimal impact on the performance, increasing the single-thread score to 1,744 (+0.8%) and the multi-thread score to 13,241 (+2.67%). This performance level is adequate for heavy multitasking. Running intensive multi-threaded applications isn't a problem, either, but know that there are significantly faster CPUs on the market. The Intel Core Ultra 7 165H is only slightly faster.
The Dell XPS 14's Intel Arc GPU scores poorly in the Basemark GPU benchmark, which isn't all that surprising, considering that it's an integrated graphics processor designed for light productivity tasks. The Ultra Performance mode boosts the score slightly to 23,062, a 5% performance increase. It can only handle light puzzle-like or older titles at 1080p with low settings. As for the NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 discrete GPU, it'll handle some demanding games at 1080p, but you'll have to play with low settings. DLSS and Frame Generation might be necessary (in supported titles) to get playable frame rates.
Models with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 GPU and/or an OLED display will have shorter battery life.
Borderlands 3 isn't playable on the Dell XPS 14 with Intel Arc graphics. The integrated GPU isn't fast enough to handle this and other similarly demanding games. You can get close to 60 fps with the lowest settings, but the gameplay is still extremely choppy. Models with an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4050 Laptop GPU will fare better and deliver more consistent frame rates, though only with low settings.
Civilization VI runs relatively well. You can easily get over 60 fps with only a few tweaks in the settings, and the average turn time is pretty decent and among the best compared to other current-gen CPUs. The RTX 4050 discrete GPU will have no problem running this game. Upgrading to the Core Ultra 7 165H won't improve the turn time significantly.
Counter-Strike 2 runs poorly on the Intel Arc integrated graphics. Although you can get over 60 fps with low settings, the gameplay isn't smooth due to frame drops. The RTX 4050 will deliver a much better experience with higher, more consistent frame rates.
Shadow of the Tomb Raider runs poorly on the Dell XPS 14 2024 with integrated graphics. You can get close to 60 fps with low settings, but the gameplay is still choppy due to frame drops. The RTX 4050 will provide a much smoother experience, with the average frame rate easily exceeding 60 fps.
The keyboard deck is only mildly warm under load, and the fan noise is low. Switching to the Ultra Performance mode doesn't impact the temperature or fan noise level. The bottom gets slightly warmer, reaching a max temperature of 38.5 °C (101.3 °F).
The Dell XPS 14 has a few pre-installed applications, including:
- Dell Digital Delivery: Lets you purchase and download software applications from Dell.
- Dell SupportAssist: Scans your computer for firmware and driver updates.
- Intel Unison: Lets you connect your smartphone to the laptop, allowing you to send and receive messages, view photos taken on your smartphone, and transfer files, similar to Windows' MyPhone app.
- Killer Intelligence Center: Lets you optimize network performance.
- McAfee: Antivirus software. Requires subscription.
- My Dell: Contains system and warranty information. Also contains various settings to apply noise cancellation during video calls, change the speakers' sound profile, calibrate the display, and change the power settings.
- Solitaire Collection: Various Solitaire-based games.
- Spotify Music: App for the music streaming service.
The Dell XPS 14 has a fingerprint sensor built into the power button and a facial recognition IR camera. You can use either to log in quickly, authorize purchases in the Windows Store, and auto-fill saved passwords on supported websites.
Comments
Dell XPS 14 (2024): Main Discussion
Let us know why you want us to review the product here, or encourage others to vote for this product.
Update: We’ve added a comparison between these buds and the Beats Studio Buds + True Wireless in Noise Isolation.
- 32120
The Nothing ear (1) case also had wireless charging, this review seems to imply otherwise.
The full review has been posted here. Let us know what you think!
- 21010
Hello. Nothing Ear 2 are headphones praised by many and I want to buy them but I’m waiting for your review, especially the quality of the calls interests me. If you guys say they are good headphones for calls then I buy them.
Our testers have started testing this product; is there anything specific you’re looking to see? Let us know in this thread.
- 32120
The Nothing ear (1) case also had wireless charging, this review seems to imply otherwise.
The full review has been posted here. Let us know what you think!
- 21010
Hello. Nothing Ear 2 are headphones praised by many and I want to buy them but I’m waiting for your review, especially the quality of the calls interests me. If you guys say they are good headphones for calls then I buy them.
Our testers have started testing this product; is there anything specific you’re looking to see? Let us know in this thread.