- Table of Contents
- Intro
- When It Matters
- Our Tests
- Additional Information
- Conclusion
- Comments
- 35.0%Megapixels
- 65.0%Pixel Density
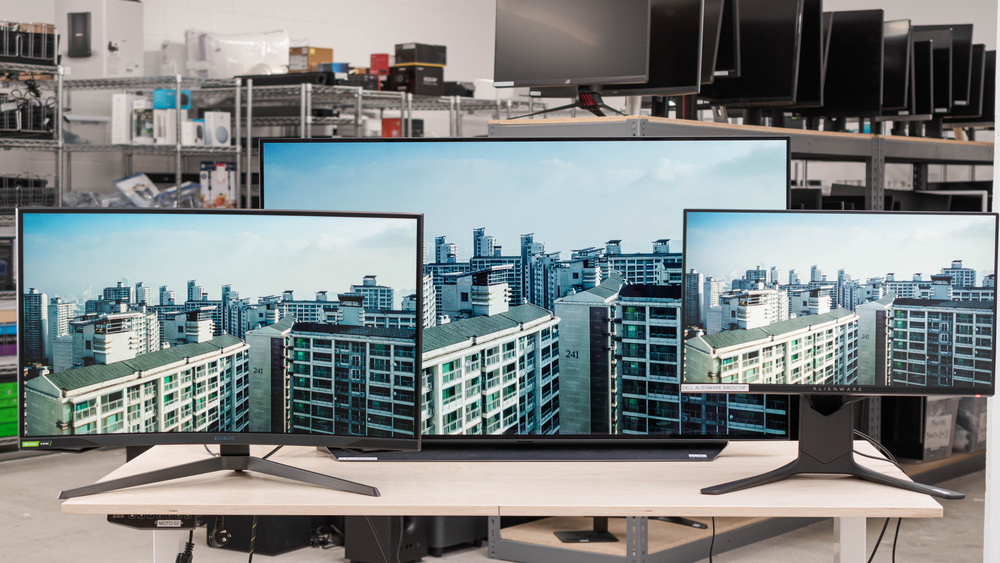
A monitor's resolution can impact your buying decision, but choosing the right one is a personal preference. Monitors are available in a few different common resolutions, like 1080p, 1440p, and 4k, and a higher resolution results in a sharper and more detailed than a lower resolution on a screen of the same size.
Our Resolution test is rather simple. We list the native resolution, aspect ratio, megapixels, and pixel density, which can help you choose a monitor.
Learn about the difference between 1080p, 1440p, and 4k here.
Test results
When It Matters
When purchasing a monitor, the first thing you may notice on its product page, or even in the model name, is what resolution it has. Choosing the right resolution really is a personal preference, as some people may prefer one resolution over the other. However, getting a high resolution can benefit some people for certain usages. For example, a higher resolution helps deliver sharper text and lets you see more content at once versus a monitor with a lower resolution, which is ideal for office use or content creation.
There are also benefits to getting a high resolution for gaming, as it delivers more detailed and realistic images. However, higher resolutions also require more bandwidth, so you may prefer gaming at a lower resolution so that it's less demanding on your graphics card.
Our Tests
For our resolution test, we look at a few things, and most of them are related to each other. We don't actually measure anything; instead, we use calculations to come up with the pixel density and megapixels.
Resolution
A screen's resolution refers to the amount of horizontal and vertical pixels within the panel; a monitor with a 1920x1080 resolution has 1920 horizontal pixels and 1080 vertical pixels. Most monitors use three common resolutions: 1080p, 1440p, and 4k, but there are also ultrawide monitors with 3440x1440 and 5120x1440, or the less common 3840x1600 and 5120x2160, resolutions.
There are often marketing terms associated with each resolution, which may be confusing and don't always refer to the same thing. For example, 4k refers to the number of horizontal pixels, while 1080p refers to the number of vertical pixels. You can see the differences between each of the common resolutions, including their marketing names.
| Name | Alt. Names | Resolution | Horizontal Pixels | Vertical Pixels |
| 1080p | Full HD FHD |
1920x1080 | 1920 | 1080 |
| 1440p | Quad HD QHD |
2560x1440 | 2560 | 1440 |
| 4k | 2160p Ultra HD UHD |
3840x2160 | 3840 | 2160 |
| 5k | - | 5120x2880 | 5120 | 2880 |
There are also ultrawide monitors that either increase the number of vertical pixels or horizontal pixels compared to the resolutions above. Most ultrawide monitors have a vertical resolution of 1440 pixels, so they're also known as 1440p, but there are some with the same vertical or horizontal resolution as 4k monitors. You can see the most common ultrawide resolutions below.
| Name | Resolution | Horizontal Pixels | Vertical Pixels |
| WQHD | 3440x1440 | 3440 | 1440 |
| WQHD | 5120x1440 | 5120 | 1440 |
| WQHD+ | 3840x1600 | 3840 | 1600 |
| 5k2k | 5120x2160 | 5120 | 2160 |
Aspect Ratio
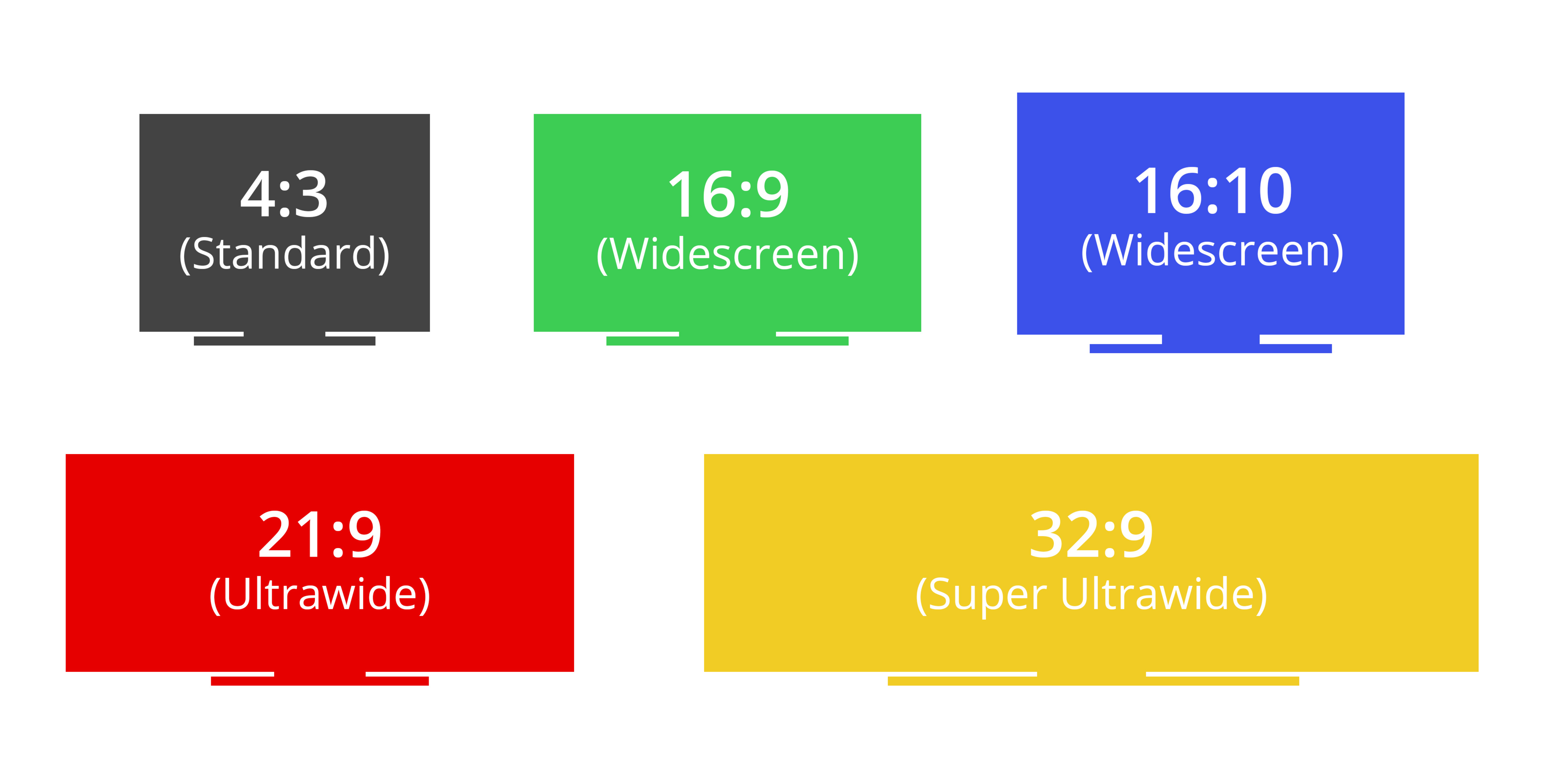
The aspect ratio refers to the ratio of horizontal pixels versus vertical pixels, and it also indicates the monitor's shape. The earliest monitors had a 4:3 aspect ratio and looked like squared screens, but this aspect ratio isn't very common anymore. Monitors have become wider; most now use a standard 16:9 aspect ratio. This means that the amount of horizontal pixels is about 1.78 times the amount of vertical pixels. However, ultrawide monitors increase the amount of horizontal space and can go up to a 21:9 or 32:9 aspect ratio. You can see the differences below.
| Aspect Ratio | Name | Resolution(s) |
| 4:3 (1.33:1) | Fullscreen | 640x480, 960x720, 1280x960 |
| 16:9 (1.78:1) | Widescreen | 1920x1080, 2560x1440, 3840x2160, 5120x2880 |
| 16:10 (1.6:1) | Widescreen | 1920x1200, 2560x1600 |
| 21:9 (2.33:1) | Ultrawide | 3440x1440, 3840x1600, 5120x2160 |
| 32:9 (3.56:1) | Super Ultrawide | 5120x1440 |
You'll notice that not all ultrawide screens have an aspect ratio of exactly 2.33:1. A 3440x1440 screen has a ratio of 2.38:1, while a 3840x1600 screen has a ratio of 2.4:1. Overall, the aspect ratio helps describe the shape of the screen, and you can see the different shapes below.
Megapixels
The amount of megapixels (MP), or millions of pixels, is simply the number of pixels in a screen. It comes from multiplying the amount of horizontal and vertical pixels, which is then divided by 1 million to give the number of megapixels - mega is another way of saying million. For example, a 4k monitor with 3840 horizontal pixels and 2160 vertical pixels has 8,294,400 individual pixels, so it has 8.3 megapixels after rounding. Simply put, the higher resolution means more pixels.
Pixel Density
Lastly, we calculate the pixel density, which represents the amount of pixels in a certain area of the screen, and the unit we measure it in is pixels per inch (PPI). We use the screen's physical measurements and its resolution to determine the PPI.
Using the advertised screen size, we can calculate the pixel density by dividing the diagonal resolution by the screen size. For example, a 4k monitor has a diagonal resolution of 4,405.814 pixels, and if the diagonal screen size is 27 inches, then the pixel density is about 164 PPI. You can also calculate the PPI2, which is the number of pixels per square inch, by dividing the megapixels by the screen area, but we don't calculate this. Below are some popular monitor sizes and their PPI.
| Diagonal Size | Resolution | Horizontal Pixels | Vertical Pixels | Width (Typical) | Height (Typical) | PPI |
| 24" | 1080p | 1920 | 1080 | 20.9" | 11.8" | 92 |
| 27" | 1080p | 1920 | 1080 | 23.5" | 13.2" | 82 |
| 27" | 1440p | 2560 | 1440 | 23.5" | 13.2" | 109 |
| 27" | 4k | 3840 | 2160 | 23.5" | 13.2" | 163 |
| 27" | 5k | 5120 | 2880 | 23.5" | 13.2" | 218 |
| 32" | 1440p | 2560 | 1440 | 27.9" | 15.7" | 93 |
| 32" | 4k | 3840 | 2160 | 27.9" | 15.7" | 138 |
| 34" | 1440p | 2560 | 1440 | 31.5" | 13.2" | 110 |
| 38" | 4k | 3840 | 1600 | 34.6" | 14.4" | 111 |
| 40" | 5k2k | 5120 | 2160 | 37.0" | 15.5" | 140 |
| 49" | 1440p | 5120 | 1440 | 47" | 13.2" | 109 |
Additional Information
Impact On Text Clarity
A monitor's resolution, and in turn, PPI, greatly affects the text clarity. The more pixels there are, the easier it is to deliver clear and sharp text. Although pixel density isn't the only deciding factor in text clarity, a monitor with a higher pixel density generally has clearer text than one with a lower pixel density. You can see examples of two 27-inch monitors below, with the left being a 1080p monitor and the right being a 4k monitor; both have Windows ClearType disabled. As you can see, the text on the right is visibly bolder, especially on diagonal lines, making it easier to read.
Having a high pixel density may not necessarily be a good thing because the higher the pixel density, the smaller the text. 4k monitors result in such fine text that you may need to increase the scaling in your system's settings to make the text legible. This is one of the reasons why resolution really is a personal preference, as some people don't mind this, while others may not prefer such a high resolution.
Conclusion
A monitor's resolution is one of the first things we consider when shopping for a new monitor. The resolution is how many pixels there are in the panel, and it helps define how clear and detailed images appear. We use the monitor's resolution and size to calculate its pixel density and the number of total pixels it has, also known as megapixels. There's no perfect resolution for everyone, as choosing one depends on your needs. Gamers tend to go for lower-resolution screens, while people using them for office work may prefer a higher resolution.
Comments
Our Monitor Input Tests: Resolution: Main Discussion
What do you think of our article? Let us know below.
Want to learn more? Check out our complete list of articles and tests on the R&D page.
- 21010
32" 1440p 2560 1440 27.9" 15.7" ppi: 93
34" 1440p 2560 1440 31.5" 13.2" ppi: 110
Before I do the math… This article is saying that a particular monitor with a greater diagonal has a smaller area when compared to a particular monitor with a shorter diagonal. I’m trying to think if it’s mathematically possible, and I think the answer could be yes. So 32" 16:9 (438.03 inches squared) is greater in area than a 34" 21:9 (415.8 inches squared). The later is not quite 21:9. So hard to do this on a phone. I gotta put a pin in this for later. If someone can help me understand…
- 21010
There is a mistake in your table with monitor sizes: 49" 1440p 5120 1440 47" 13.2" 109 Should be: 49" 1440p 2560 1440 47" 13.2" 60
Hello,
There are 49-inch monitors with a 5120x1440 resolution, which have a pixel density of 109. They’re still considered 1440p (because of the vertical resolution), and there aren’t any 2560x1440 49-inch monitors available.
- 21010
There is a mistake in your table with monitor sizes:
49" 1440p 5120 1440 47" 13.2" 109
Should be:
49" 1440p 2560 1440 47" 13.2" 60